

|
19.213 bytes |
Product Information |
Document ID: DDSE-42CSMN |
Netfinity 3000 - Configuration Conflicts
Applicable to: World-Wide
Configuration Conflicts
The resources used by your server consist of IRQs, DMA, I/O port addresses, and memory. This information is
useful when a resource configuration conflict occurs.
Conflicts in the configuration occur if:
- A device that you installed requires the same resource as another device. (For example, a conflict occurs when two adapters try to write to the same address space.)
- A device resource is changed (for example, changing jumper settings).
- A device function is changed (for example, assigning COM1 to two serial ports).
- A software program is installed that requires the same resource as a hardware device.
The steps required to resolve a configuration error are determined by the number and variety of hardware devices
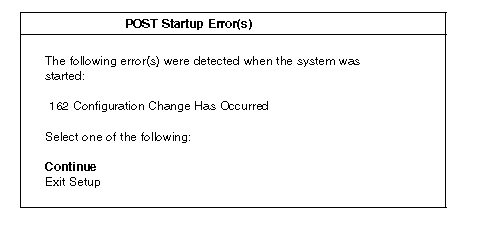
and software programs that you install. If a hardware configuration error is detected, a configuration error message appears after the server completes POST and before the operating system is loaded. You can bypass the error by pressing Esc while the error message is displayed.
The Configuration/Setup Utility program configures only the system hardware and interrupt requests. The program
does not consider the requirements of the operating system or the application programs. For these reasons,
memory-address configuration conflicts might occur. You can resolve some memory-address conflicts by changing
the address of the conflicting hardware option, or by changing or moving the hardware. You might have to
resolve other memory-address conflicts by changing some software parameters. See Hardware Configuration
Conflicts and Software Configuration Conflicts on page 21, respectively, for additional information.
Hardware Configuration Conflicts
Use the following information to help resolve hardware configuration conflicts:
1. Run the Configuration/Setup Utility program to view and change the resources that the system board functions use. Record the current settings before making any changes. (See "Configuration/Setup Utility Program" for instructions.)
2. Determine which adapter or device is causing the conflict.
3. Change adapter jumpers or switches. Some devices use jumpers and switches to define the system resources that they need. If the settings are incorrect or set to use a resource that cannot be shared, a conflict occurs, and the device will remain deactivated by the configuration program.
4. Change system board jumpers or switches. Then, refer to the system-board diagram inside your server.
5. Remove the device or adapter. Some configurations are not supported. If you must remove an adapter, see "Installing or Removing ISA and PCI Adapters".
Software Configuration Conflicts
The Configuration/Setup utility might change the memory-address space used by some hardware options. If this happens, the new memory-address space and IRQs used by some hardware options might conflict with addresses defined for use through application programs.
If a conflict exists, one or more of the following conditions might exist:
- The system cannot load the operating system.
- The system does not work.
- An application program does not operate, or it returns an error.
- Screen messages indicate that a memory-address conflict exists.
|
Note |
|
Note |
|
Notes |
|
Search Keywords |
| |
|
Document Category |
Configuration | |
|
Date Created |
18-11-98 | |
|
Last Updated |
23-11-98 | |
|
Revision Date |
18-11-99 | |
|
Brand |
IBM PC Server | |
|
Product Family |
Netfinity 3000 | |
|
Machine Type |
8476 | |
|
Model |
ALL | |
|
TypeModel |
| |
|
Retain Tip (if applicable) |
| |
|
Reverse Doclinks |