

|
49.849 bytes |
Service Hints & Tips |
Document ID: GSMH-3E8G6D |
PC Server 330 - RAID Technology
Applicable to: World-Wide
RAID Technology:
RAID is the technology of grouping several hard disk drives in a server into an array that can be defined as a single logical drive. This logical drive then appears to the operating system as a single physical drive. This grouping technique greatly enhances logical-drive capacity and performance. In addition, if one of the hard-disk drives fails (becomes defunct) the system continues to run, with no operator intervention required, at reduced performance. You can replace the defunct drive without powering off the server ( hot-swap ). For more information about hot-swappable hard disk drives, refer to the internal drive installation information (Internal Drives, Internal Drive Bays, or Installing internal Drives) in your IBM PC Server Hardware Maintenance Manual (form number S30H-2501-01).
Hard Disk Drive Capacities:
The drives in the disk array can be of different capacities (for example, 1 GB or 2 GB); however, they are treated in the disk array configuration as if they all have the capacity of the smallest disk drive. Therefore, if you have four drives of 1 GB, 1 GB, 1 GB, and 2 GB grouped in one disk array, the total capacity of the array is 1 GB times 4, or 4 GB (instead of the 5 GB physically available).
|
Notes: |
Additional Storage Capacity:
With the Administration and Monitoring program Remote Monitor, you can dynamically add capacity to the server by defining additional arrays and logical drives (when the operating system supports this). When you use the Remote Monitor, you do not have to restart the server to create an array.
When hard disk drives are added to the server, a new disk array must be configured before the drives can be used. Reconfigure the existing disk array to include the capacity offered with the added drives, or group the added drives into their own array (see 'Creating a Disk Array—).
|
Note: |
ServeRAID Configuration Program Screens:
Use the IBM ServeRAID configuration program on the Array Configuration (also called the ServeRAID Configuration) diskette to configure or view the disk array. The following example screen is a compilation of many of the IBM ServeRAID Controller Disk Array Configuration (also called the ServeRAID configuration program) screens. The list that follows example explains the numbered areas of the example.
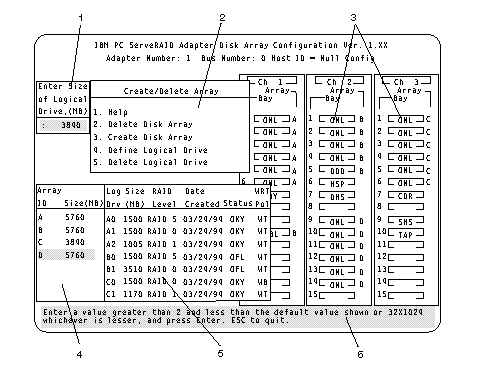
1. This area displays pop-ups that apply to the current menu. For example, a pop-up allows you to select the logical drive size by entering the size in megabytes; or, to accept the default value shown. Another pop-up allows you to select the RAID level you want to assign to the logical drive you are defining. When you need to confirm an action, the Confirm pop-up appears in this area.
2. You can select any of the choices that appear on the menus.
3. The Bay/Array selection list shows 15 bays for each of the adapter's three channels. For each bay that contains a drive, the list indicates the state of the physical drive and the array in which the drive is grouped. For example, in the illustration, the drive in Channel 2, Bay 1, has a drive status of ONL and is a part of Array B. Selections are made from this list to determine which bays (hard disk drives) are in the arrays.
|
Notes: |
4. The Array list indicates the array ID and the size (in megabytes) of the array. When a drive is being rebuilt, this area, along with the Logical Drive list area, shows the progression of the rebuilding process.
5. The Logical Drive list identifies the logical drive (for example, A1), including its size, the RAID level, date of creation, and its write policy.
The status of the logical drive also is shown.
|
OKY |
No problem conditions are associated with the drive. |
|
CRT |
Replace the defunct drive and do a rebuild operation. (You will have received a message telling you what has happened to the drive.) |
|
OFL |
The logical drive is unrecoverable; the data in that drive is lost. |
When a drive is being rebuilt, this area, along with the Array list area, shows the progression of the rebuilding process.
During an initialization process, the Write Policy area displays the percent initialized; during a synchronization process, it displays the percent synchronized.
6. The information area tells you the action you can perform on this screen or pop-up.
|
Search Keywords |
| |
|
Hint Category |
RAID, Hardware Maintenance Information | |
|
Date Created |
12-02-97 | |
|
Last Updated |
11-02-99 | |
|
Revision Date |
11-02-2000 | |
|
Brand |
IBM PC Server | |
|
Product Family |
PC Server 330, ServeRAID | |
|
Machine Type |
8640, Various | |
|
Model |
| |
|
TypeModel |
| |
|
Retain Tip (if applicable) |
N/A | |
|
Reverse Doclinks |