

|
101.546 bytes |
Parts Information |
Document ID: MCGN-44HMRM |
ServeRAID - Configuration Overview
Applicable to: World-Wide
Configuration Overview
The IBM ServeRAID Configuration Utility programs enable viewing of the current disk array configuration, the changing or deletion of existing arrays, the creation and initialization of new disk arrays, and the performance of many other configuration and maintenance tasks.
It is necessary to use a ServeRAID Configuration Utility program to configure your disk array before partitioning hard disk drives and installing an operating system. You can use the DOS Configuration Program, the GUI-Based Configuration Program, and the ServeRAID Administration and Monitoring Utility. After configuring the disk arrays and installing the operating system, return to this manual for information about installing and using the ServeRAID Administration and Monitoring Utility programs.
Using the ServeRAID DOS Configuration Program
To start the ServeRAID Configuration Utility program:
1. Insert the IBM ServeRAID Configuration Diskette into the primary diskette drive and turn on the system. If the system is already turned on, shut down and restart the system.
Each time the system starts, the PC ServeRAID Adapter performs a power-on self-test (POST). The POST checks the configuration information for the PC ServeRAID Adapter and for the configured hard disk drives.
a. If POST does not detect changes in the adapter configuration or any adapter hardware problems, continue with step b.
b. If you have multiple ServeRAID adapters installed in your system, you will see a screen with multiple adapters. The screen may not look exactly like this one.
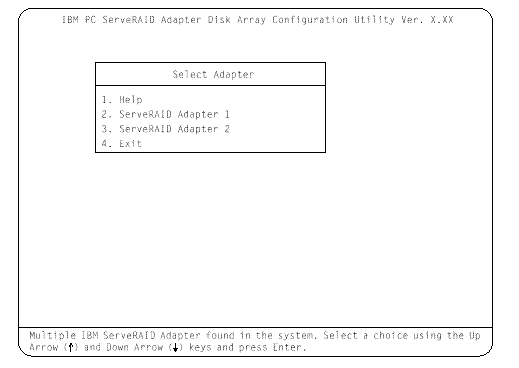
|
Note |
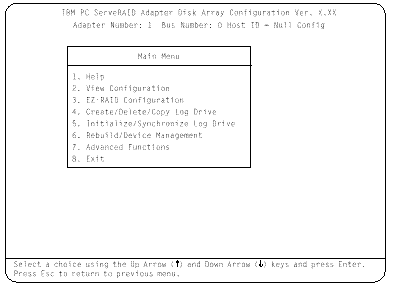
4. To choose an option from the Main Menu, type the highlighted number of the menu item, or use the Up Arrow key or Down Arrow key to highlight your choice; then, press Enter. You also can press Esc to return to the previous menu, the previous work area of a screen, or to the beginning of the Main Menu.
To restore or convert disk array information when you upgrade from an IBM PCI ServeRAID Adapter or an IBM Streaming Adapter to an IBM PC ServeRAID Adapter:
1. From the Main Menu, select Advanced Functions.
2. Select Restore/Convert Saved Config.
|
Note |
To "fine tune" the ServeRAID subsystem for optimal performance:
1. From the Main Menu, select Advanced Functions.
2. Select Change ServeRAID Parameters.
You can control the following parameters:
- Stripe unit size - defines the stripe unit size of the data close to the size of the system I/O requirements. The default setting is 8K bytes.
|
Note |
- Rebuild priority - sets the priority of the execution order of the rebuild I/O requests with respect to system I/O requests. You can change the Rebuild Priority without affecting data in the logical drives. The default setting is High.
- Unattended mode - enables/disables the PC ServeRAID Adapter or Controller to resolve configuration-related conflicts without user intervention. The default setting is Off.
- Read ahead - enables/disables the cache read ahead up to the end of the stripe unit. You can change the Read Ahead without destroying data in the logical drives. The default setting is On.
To set a basic configuration:
1. From the Main Menu, select Advanced Functions.
2. Select Init/View/Synchronize Config.
When you choose Initialize Configuration:
- all defined logical drives and arrays are deleted
- all attached drives are reset to Ready
- the configuration Host ID changes to "Null Configuration."
- "Start Device" is issued to all drives.
The PC ServeRAID Adapter stores its ServeRAID configuration in its NVRAM (Battery-Backup Cache), FLASH (EEPROM), and on all physical hard disk drives that are part of a logical drive. An option is provided to view the configuration from all of these sources.
You may also choose a source (hard disk drive, FLASH, NVRAM (Battery-Backup Cache)) from which to synchronize the ServeRAID configuration. For example, you may do this when a new ServeRAID adapter/controller is used to replace a defective one. We recommend using the hard drive, since it refreshes information in the buffers about the drive firmware levels.
The PC ServeRAID Adapter also maintains a list of all changes to its ServeRAID configuration. A power-on change list, wrong SCSI ID list, and an unidentified drive list are updated when devices are added or moved. Changes to the states of the devices also change this list. An option is provided to view all of this information.
To display the PC ServeRAID Adapter status or to write a new adapter configuration Host ID:
1. From the Main Menu, select Advanced Functions.
2. Select Display/Change Adapter Params.
You can also change the PC ServeRAID Adapter SCSI channel ID and speed.
Using the ServeRAID GUI-Based Configuration CD
To start the configuration program:
1. Insert the ServeRAID GUI-Based CD into the CD-ROM drive; then, turn on the server.
One of the following screens will appear:
- If the configuration program detects unconfigured ServeRAID controllers, the program starts in the Configuration mode and a screen similar to the following appears.
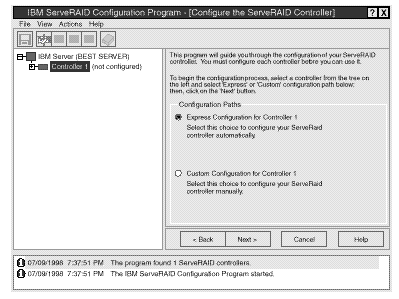
Select the Cancel button to switch from the Configuration mode to the Information mode.
- If the configuration program detects that all ServeRAID adapters or controllers in the server are configured, the program starts in the Information mode and a screen similar to the following appears.
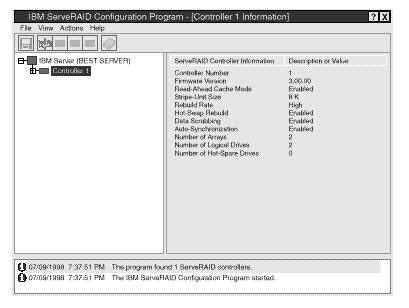
Select the  icon on the Tool Bar to switch from the Information mode to the Configuration mode.
icon on the Tool Bar to switch from the Information mode to the Configuration mode.
2. Disable or Enable Read-Ahead Cache Mode: This choice is available in the Information mode only. When read-ahead cache is set to Enabled (default setting), the ServeRAID adapter/controller transfers data from a disk to its local cache in increments equal to the stripe unit size. This provides excellent overall performance when workloads are steady and sequential. However, if the workload is random or the system I/O requests are smaller than the stripe unit size, reading ahead to the end of the stripe might degrade performance. When read-ahead cache is set to Disabled, the ServeRAID adapter/controller transfers data from a disk to local cache in increments equal to the system I/O request size, without reading ahead to the end of the stripe.
3. Change the Rebuild Rate: This choice is available in the Information mode only. You can select this choice to set the priority for Rebuild operations to High (default), Medium, or Low.
- When the rebuild rate is set to High, the rebuild I/O request gets high priority in the execution order.
- When the rebuild request is set from High to Medium in a heavily-loaded system, it can increase the rebuild time, but provide better system performance.
- When the rebuild request is set from High or Medium to Low in a moderately- to heavily-loaded system, it can increase the disk rebuild time, but provides better system performance.
|
Search Keywords |
| |
|
Document Category |
Controllers | |
|
Date Created |
26-01-99 | |
|
Last Updated |
15-03-99 | |
|
Revision Date |
15-03-2000 | |
|
Brand |
IBM PC Server | |
|
Product Family |
ServeRAID | |
|
Machine Type |
Various | |
|
Model |
| |
|
TypeModel |
| |
|
Retain Tip (if applicable) |
| |
|
Reverse Doclinks |